OT network segmentation is critical in protecting your OT environments from rising cyber threats. The average cost of a data breach—currently at $4.88 million—should strike fear into the heart of any CISO. As alarming as that figure is, it pales in comparison to the cost of production downtime. According to a 2023 Siemens report, the cost of industrial and process downtime ranges from $39,000 to more than $2 million per hour. Yes, per hour. In oil and gas, the hourly cost of downtime is almost $500,000; an automotive plant can exceed $2 million an hour in downtime costs.

Today, the risk of cybersecurity incidents and ransomware attacks can’t be ignored. Manufacturing and industrial companies need to proactively defend against a rising threat. According to the 2024 State of Operational Technology and Cybersecurity Report, 73% of OT professionals have experienced cybersecurity intrusions that affected OT systems this year—up from 49% in 2023. The good news is that the best foundation for proactive defense for OT assets can be built on OT network segmentation.
What is OT Network Segmentation, Exactly?
The 3 Main Challenges to OT Network Segmentation
1. The sheer cost
2. The legacy technology
Many OT systems are built on legacy technology and lack the digital intelligence to execute security functions. Others carry unsupported operating systems or are not updated. Some lack the compute power or bandwidth to add security agents. Still others simply can’t be patched to standards. Particularly in brownfield OT networks, until recently, it was just not possible to add security solutions independently of existing infrastructure without significant downtime.
Traditional IT segmentation solutions can’t be easily extended to an OT environment because they simply don’t speak the same languages.
3. The disconnect between IT and OT security teams
A New Approach to OT Segmentation
Industrial organizations find themselves between a rock and a hard place, but there is a way to implement OT segmentation while minimizing the risk of downtime and a cyber breach.
“Non-invasive” OT segmentation enables you to implement defenses and simultaneously lay the groundwork for important capabilities such as:
-
-
- Managing asset inventory
- Implementing network visibility tools
- Identifying places where assets should be isolated
- Implementing least privilege functionality
- Managing control of privileged access
- Managing remote access to security zones and assets
-
Using the ISA/IEC 62443 Standards for Planning OT Segmentation
IT/OT Segmentation
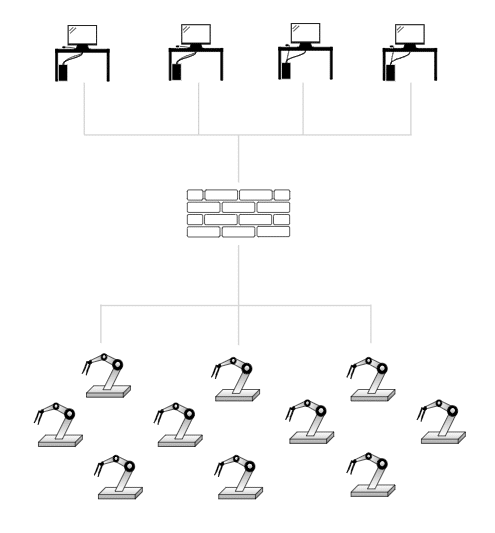
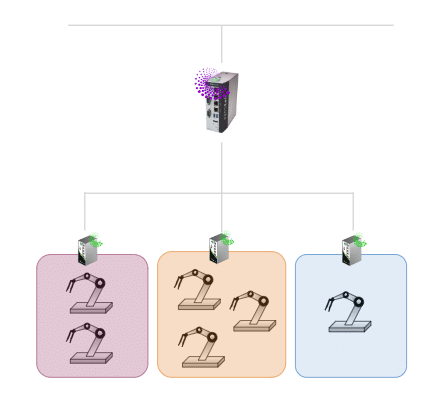
Zone or Cell Segmentation
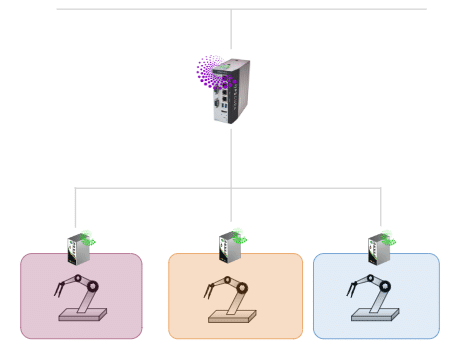
Micro-Segmentation
4 Easy Steps to OT Segmentation
Step 1: Combine Perspectives
Step 2: Define Security Challenges
Step 3: Align Implementation Objectives
Third, align on objectives. Prioritize the criticality of each process and the implications of a breach – especially the cost of downtime – for these processes. Highlight the zones or assets that would most benefit from cloaking.
As you walk through your home, think about the spaces and things you would want to make impenetrable or, better yet, invisible to intruders. That’s segmentation and micro-segmentation.
Step 4: Leverage Experience
Bonus Step: Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
Software-defined networking (SDN)-based solutions create a virtual overlay of the OT network. This enables organizations to implement non-invasive, virtual OT segmentation tailored to their business needs and security requirements—quickly and without downtime or disruption. By decoupling network control and forwarding functions from physical hardware, such as routers and switches, you can not only create a more manageable and dynamic network infrastructure, but also eliminate the need to reconfigure any industrial asset like a PLC. This can save the pains of more than a year of planning and $100,000’s of planned downtime.
How Opscura can Help
Successful OT segmentation projects in manufacturing, energy, transportation and other critical industries are relying on the Opscura OT Security Protection Platform for their lightweight yet effective segmentation and Software Defined Network (SDN) implementations.
These customers have gained:
-
-
-
Software-based solutions: Opscura functions as an SDN overlay to existing networks, eliminating the cost and disruption associated with adding or re-engineering systems, IP addressing, or networks.
-
Rapid deployment without disruption: Deployment takes just hours—instead of weeks—without requiring committed IT networking experts. Protection is immediate and automatic with no downtime or impact on shop floors or processes.
-
Leading-edge security for OT assets: Opscura provides immediate, automatic zero trust access to OT assets through segmentation with complete transparency to existing OT and IT systems. Organizations can authenticate access by zone or cell with highly specific granularity. Patented data stream encryption technology secures OT network data traveling over the network with <1ms latency. Opscura’s patented network device security system and methodology also enable network appliances to self heal. For the first time, organizations have a unified, consistent way to secure every zone and asset.
-
Asset cloaking: Bad actors can’t attack what they can’t see. For systems that can’t be patched or updated, Opscura cloaks traffic from observation to thwart attacker discovery and reconnaissance. Organizations can still protect their environments even though vulnerabilities might remain.
-
-
